Abstract
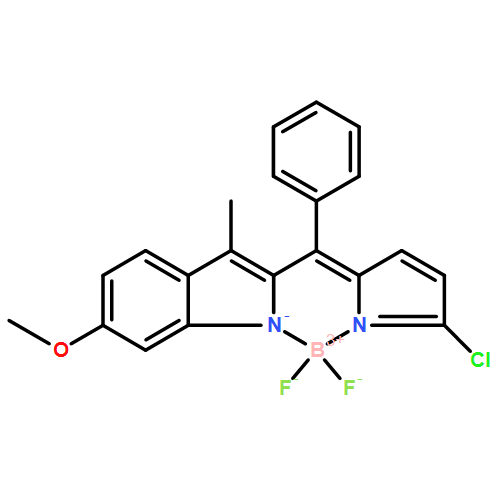
The simultaneous discrimination of Cys, Hcy, and GSH by a single probe is still an unmet challenge. The design and synthesis of a small molecule probe MeO-BODIPY-Cl (BODIPY=boron dipyrromethene) is presented, which can allow Cys, Hcy, and GSH to be simultaneously discriminated on the basis of three distinct fluorescence turn-on responses. The probe reacts with these thiols to form sulfenyl-substituted BODIPY, which is followed by intramolecular displacement to yield amino-substituted BODIPY. The kinetic rate of the intramolecular displacement reaction determines the observed different sensing behavior. Therefore, the probe responds to Cys, Hcy, and GSH with fluorescence turn-on colors of yellow, yellow and red, and red, respectively. With this promising feature in hand, the probe was successfully used in imaging of Cys, Hcy and GSH in living cells.