Abstract
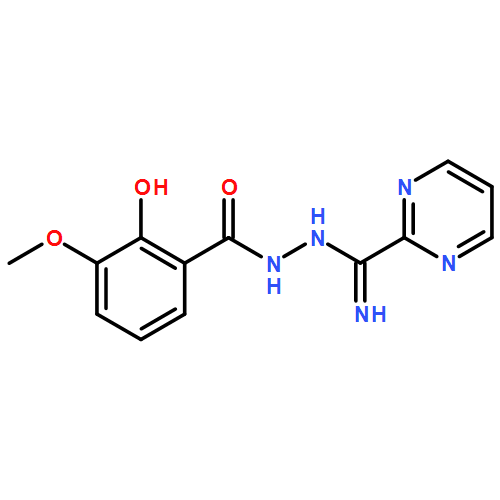
Efficient modulation of single-molecule magnet (SMM) behavior was realized by deliberate structural modification of the Dy2 cores of [Dy2(a′povh)2(OAc)2(DMF)2] (1) and [Zn2Dy2(a′povh)2(OAc)6]⋅4 H2O (2; H2a′povh=N′-[amino(pyrimidin-2-yl)methylene]-o-vanilloyl hydrazine). Compound 1 having fourfold linkage between the two dysprosium ions shows high-performance SMM behavior with a thermal energy barrier of 322.1 K, whereas only slow relaxation is observed for compound 2 with only twofold connection between the dysprosium ions. This remarkable discrepancy is mainly because of strong axiality in 1 due to one pronounced covalent bond, as revealed by experimental and theoretical investigations. The significant antiferromagnetic interaction derived from bis(μ2-O) and two acetate bridging groups was found to be crucial in leading to a nonmagnetic ground state in 1, by suppressing zero-field quantum tunneling of magnetization.