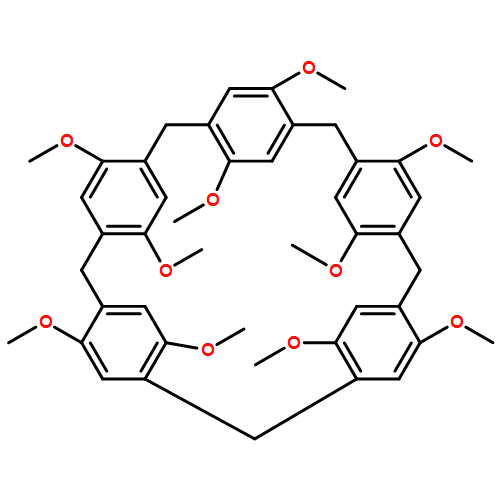
Abstract
To clarify the binding mechanisms and driving forces for the unique ability of pillar[5]arenes to recognize neutral molecules, the complexation of a series of nitrogen heterocycle substituted 1,4-butylene guests with pillar[5]arenes was studied. Guests molecules that have similar structures exhibit remarkably different association constants, and multiple weak C–H···N interactions between the alkyl groups of the pillar[5]arenes and the outer nitrogen atoms of the heterocycles of the guests are the dominant driving forces for complexation.