BASIC PARAMETERS Find an error
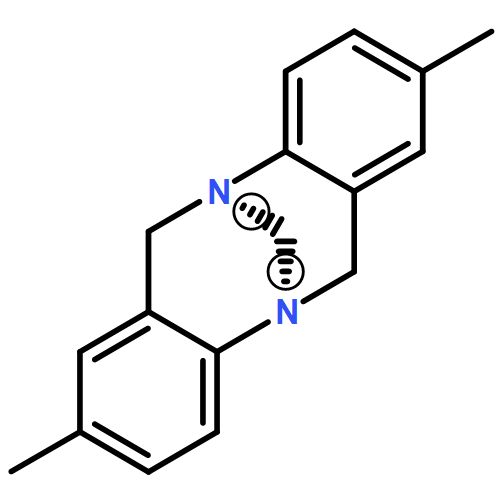
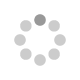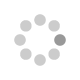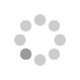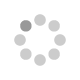
Seven racemic derivatives of Tröger’s base—the 1,7-dibromo-substituted derivative 3, the 2,8-dibromo-substituted derivative 4, the 2,8-diiodo-substituted derivative 5, the 3,9-diiodo-substituted derivative 6, the 4,10-dibromo-substituted derivative 7, its singly debrominated analogue 8, and the 2,8-diamino-substituted derivative 9 in its Fmoc-protected form—were synthesized and successfully resolved by (recycling) HPLC on a stationary Whelk-O1 phase at a semipreparative scale. These are valuable functionalized C2-symmetric building blocks for further applications. Their absolute configurations were determined by X-ray crystal structure analysis and/or by comparison of their quantum chemically calculated circular dichroism and UV/Vis spectra with the experimental obtained spectra.
Chromatographic enantioseparations on the order of a few seconds can be achieved by supercritical fluid chromatography using short columns packed with chiral stationary phases. The evolution of ‘world record’ speeds for the chromatographic separation of enantiomers has steadily dropped from an industry standard of 20–40 min just two decades ago, to a current ability to perform many enantioseparations in well under a minute. Improvements in instrument and column technologies enabled this revolution, but the ability to predict optimal separation time from an initial method development screening assay using the tmin cc predictor greatly simplifies the development and optimization of high-speed chiral chromatographic separations. In this study, we illustrate how the use of this simple tool in combination with the workhorse technique of supercritical fluid chromatography on customized short chiral columns (1–2 cm length) allows us to achieve ultrafast enantioseparations of pharmaceutically relevant compounds on the 5–20 s scale, bringing the technique of high-throughput enantiopurity analysis out of the specialist realm and into the laboratories of most researchers.
Chromatographic enantioseparations on the order of a few seconds can be achieved by supercritical fluid chromatography using short columns packed with chiral stationary phases. The evolution of ‘world record’ speeds for the chromatographic separation of enantiomers has steadily dropped from an industry standard of 20–40 min just two decades ago, to a current ability to perform many enantioseparations in well under a minute. Improvements in instrument and column technologies enabled this revolution, but the ability to predict optimal separation time from an initial method development screening assay using the tmin cc predictor greatly simplifies the development and optimization of high-speed chiral chromatographic separations. In this study, we illustrate how the use of this simple tool in combination with the workhorse technique of supercritical fluid chromatography on customized short chiral columns (1–2 cm length) allows us to achieve ultrafast enantioseparations of pharmaceutically relevant compounds on the 5–20 s scale, bringing the technique of high-throughput enantiopurity analysis out of the specialist realm and into the laboratories of most researchers.
Ten novel xylan bisphenylcarbamate derivatives bearing meta- and para-substituents on their phenyl groups were synthesized and their chiral recognition abilities were evaluated as the chiral stationary phases (CSPs) for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) after coating them on macroporous silica. The chiral recognition abilities of these CSPs depended on the nature, position, and number of the substituents on the phenyl moieties. The introduction of an electron-donating group was more attractive than an electron-withdrawing group to improve the chiral recognition ability of the xylan phenylcarbamate derivatives. Among the CSPs discussed in this study, xylan bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate)-based CSP seems to possess the highest resolving power for many racemates, and the meta-substituted CSPs showed relatively better chiral recognition than the para-substituted ones. For some racemates, the xylan bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) derivative exhibited higher enantioselectivity than the CSP based on cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate). Chirality 27:518–522, 2015 © 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Ten novel xylan bisphenylcarbamate derivatives bearing meta- and para-substituents on their phenyl groups were synthesized and their chiral recognition abilities were evaluated as the chiral stationary phases (CSPs) for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) after coating them on macroporous silica. The chiral recognition abilities of these CSPs depended on the nature, position, and number of the substituents on the phenyl moieties. The introduction of an electron-donating group was more attractive than an electron-withdrawing group to improve the chiral recognition ability of the xylan phenylcarbamate derivatives. Among the CSPs discussed in this study, xylan bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate)-based CSP seems to possess the highest resolving power for many racemates, and the meta-substituted CSPs showed relatively better chiral recognition than the para-substituted ones. For some racemates, the xylan bis(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) derivative exhibited higher enantioselectivity than the CSP based on cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate). Chirality 27:518–522, 2015 © 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
The classical method for the preparation of immobilized polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases (CSPs) with a diisocyanate was improved. Cellulose or amylose was directly coated onto 3-aminopropyl silica gel after it was dissolved in a mixture of N,N-dimethylacetamide, LiCl, and pyridine, then immobilized onto silica gel with a diisocyanate, and finally allowed to react with an excess of corresponding isocyanate. Four polysaccharide derivatives, 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate and 3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate of cellulose, and 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate and 5-chloro-2-methylphenylcarbamate of amylose, were immobilized onto silica gel utilizing this method. Compared with the classical diisocyanate method, the improved procedure avoided the derivatization and regeneration of 6-hydroxyl groups of cellulose and amylose, and thus showed an advantage for simple and economical preparation. The relationships among the amount of diisocyanate used, immobilization efficiency, and enantioseparation on the cellulose-based CSPs were investigated. Also, the solvent durability of the obtained CSPs was examined with eluents containing chloroform or THF. By utilizing these eluents, the chiral recognition abilities of the obtained CSPs for some of the tested racemates were improved.