Co-reporter: Jinxin Lu, Chengdong Sun, Wei Chen, Huimin Ma, Wen Shi, Xiaohua Li
pp: 1050-1056
Publication Date(Web):15 January 2011
DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2010.11.023
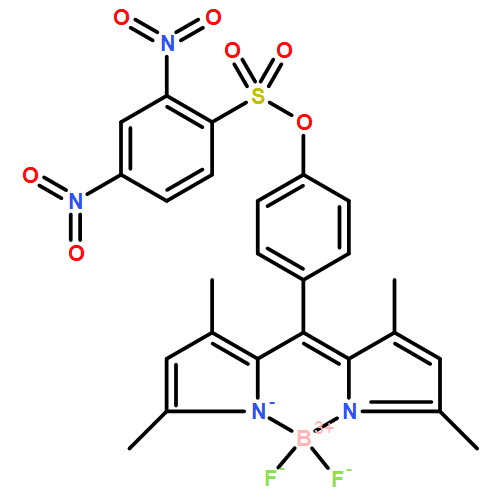
A novel fluorescent probe is designed and synthesized for the determination of cysteine in biological samples by incorporating 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl (DBS) group as a quencher into the BODIPY skeleton. The BODIPY-based probe itself shows weak fluorescence due to the strong intramolecular charge transfer process. Upon reaction with cysteine, however, the probe produces a rapid and large fluorescence enhancement through the removal of the DBS unit by nucleophilic aromatic substitution. This valuable property leads to the development of a new and simple method for cysteine assay. Under the optimized conditions, the fluorescence enhancement value is directly proportional to the concentration of cysteine in the range 2–12 μM, with a detection limit of 30 nM (S/N = 3). The applicability of the developed method has been successfully demonstrated on the determination of non-protein cysteine in human serum. Compared to most of the existing fluorescent probes proposed for cysteine, the BODIPY-based one exhibits an excellent overall performance in terms of selectivity, sensitivity and simplicity.