Abstract
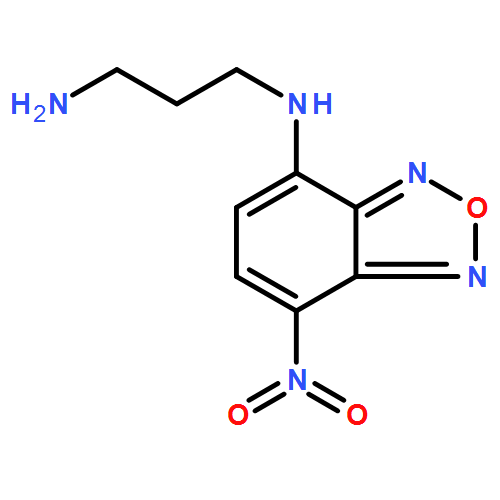
The binding behavior of green fluorescent ligands, derivatives of 7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD), with DNA duplexes containing an abasic (AP) site is studied by thermal denaturation and fluorescence experiments. Among NBD derivatives, N1-(7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diamine (NBD-NH2) is found to bind selectively to the thymine base opposite an AP site in a DNA duplex with a binding affinity of 1.52×106 M−1. From molecular modeling studies, it is suggested that the NBD moiety binds to thymine at the AP site and a protonated amino group tethered to the NBD moiety interacts with the guanine base flanking the AP site. Green fluorescent NBD-NH2 is successfully applied for simultaneous G>T genotyping of PCR amplification products in a single cuvette in combination with a blue fluorescent ligand, 2-amino-6,7-dimethyl-4-hydroxypteridine (diMe-pteridine).