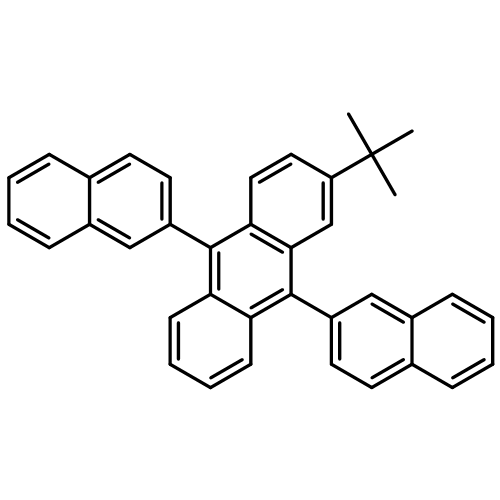
Small molecular organic light-emitting diodes (SMOLEDs) were fabricated with an ink-jet printed film of 2-(t-butyl)-9,10-bis (20-naphthyl) anthracene (TBADN) doped with 4,4′-bis[2-{4-(N,N-diphenylamino)phenyl vinyl] (DPAVBi) as emitting layer. Dewetting behavior of ink-jet printed TBADN/DPAVBi solutions were restrained by adding cyclohexylbenzene or α-chloronaphthalene to the main solvent chlorobenzene. The high boiling point and high viscosity of cyclohexylbenzene and α-chloronaphthalene has increased the thickness of liquid films and the viscosity, which restrained the dewetting from thermodynamics and kinetics aspect. Uniform TBADN/DPAVBi films obtained by ink-jet printing from chlorobenzene/cyclohexylbenzene solution have been used in the fabrication of matrix display of SMOLEDs. The OLEDs has a turn-on voltage of 5.5 V, the maximum luminance of 289 cd/m2 and the maximum current efficiency of 0.71 cd/A.Graphical abstract

Research highlights► Uniform and pinhole free TBADN/DPAVBi films were deposited by inkjet printing. ► High boiling point and high viscosity solvents improved film forming property. ► Dewetting of TBADN/DPAVBi films restrained from thermodynamics and kinetics aspect. ► Inkjet printed TBADN/DPAVBi films were used to fabricate electroluminescent devices.