Co-reporter: Chunkai Wang, Feifei Xing, Yue-Ling Bai, Yongmei Zhao, Ming-Xing Li, and Shourong Zhu
pp: 2277-2288
Publication Date(Web):March 9, 2016
DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00065
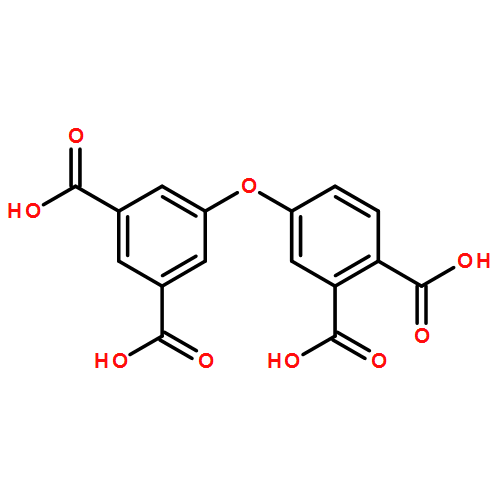
Three porous Cu(II) coordination polymers {[(CH3)2NH2]3[Cu7K(μ7-L1)2(μ7-L1)2(μ2-OH)2(H2O)6]·18H2O}3n (1), {[Cu5(μ8-L1)2(μ3-OH)2(H2O)5]·4.5DMF·18H2O}3n (2), {[Cu5(μ8-L2)2(μ3-OH)2(H2O)4]·DMF·10.5H2O}3n (3), where KH3L1 and H4L2 are semirigid 3-(3′,5′-dicarboxylphenoxy) phthalic acid and 4-(3′,5′-dicarboxylphenoxy) phthalic acid, respectively, were synthesized solvothermally. Their guest-accessible voids are 36%, 59%, and 39% in 1, 2, and 3, respectively. These three porous coordination polymers show high catalytic activities for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB), methylene blue (MB), safranine T (ST), and orange II (OII) dyes in aqueous solution. The reaction kinetics follow v = k[H2O2][RhB], where k = 0.0260 ± 0.001 L·mol–1·min–1 in the presence of 3, while 1 and 2 follow v = [H2O2][RhB]/(1/kK + (1/k)[H2O2]), where K = 5.0 ± 0.5 M–1, k = 0.057 ± 0.007 min–1 for 1 and K = 4.5 ± 0.5 M–1, k = 0.083 ± 0.009 min–1 for 2 at pH 7.0. All three catalysts show good catalytic activity in pH 4.8–8 and are essentially constant in this pH range while further increases will decrease catalytic activity. Complexes 1 and 3 exhibited good structural stability in the catalytic process with no discernible catalytic activity decrease after three catalytic cycles. Complex 2 is unstable in the catalytic process. MS data show that the slow catalyst 3 degrades RhB into aromatic carboxylate. Faster 1 further degrades RhB into aromatic and aliphatic carboxylate, while fastest 2 not only degrades RhB, but also the catalyst itself. These catalysts not only degrade RhB but also methylene blue, saframine T, and orange II. Azo dye orange II was oxidized into red nitrosobenzene and then degraded nitrisobenzene into colorless species. Complex 1 has the advantage of good catalytic activity, stability, and availability. Along with ease of recovery, it will be useful in practical applications.