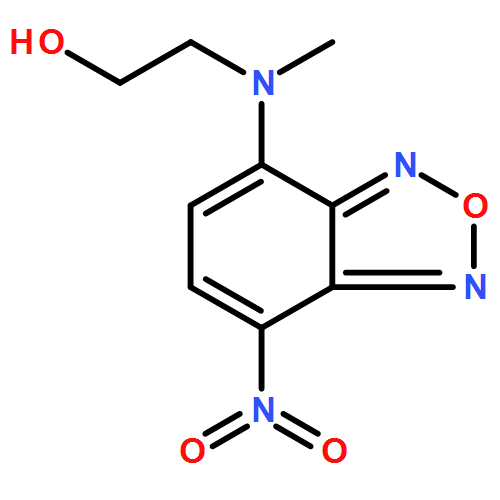
A series of different copolymers of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, AMPS, and butyl methacrylate, BuMA, were prepared by free radical polymerization at 70°C in N,N ′-dimethylformamide under nitrogen atmosphere varying the composition feed. The polyamphiphiles isolation was carried out by passing the polymeric solutions through a sodium cation exchange resin. The stabilities of the obtained homopolymers and copolymers were characterized by thermal analysis (TGA, DSC). Fluorescent probes were used to study the hydrophobic microdomain formation due to the association phenomena observed in water solution when the amphiphilic copolymer concentration was increased. The fluorescence emission of amino derivatives of 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD) showed sensitivity to detect polarity and microviscosity changes in the microenvironment of the copolymers. The minimum concentration for the hydrophobic microdomains formation, Cm , decreased by increasing the molar fraction of BuMA in the AMPSCo copolymers. Hence, copolymer composition and charge density allowed tuning the pseudo-micellar characteristics of these new polyamphiphilic copolymers.